China Global Growth Tendencies
Shaping the Future
China, a nation once known for its ancient history and rich cultural heritage, has rapidly transformed into one of the most influential global players in the 21st century. Its emergence as an economic powerhouse is not merely a reflection of its vast population or historical legacy, but rather the result of strategic investments, innovative advancements, and a commitment to reshaping the global economic and political landscape. Understanding the growing tendencies of China in the global arena offers valuable insight into the nation’s future trajectory and its potential to influence world affairs.
Economic Growth and Global Influence
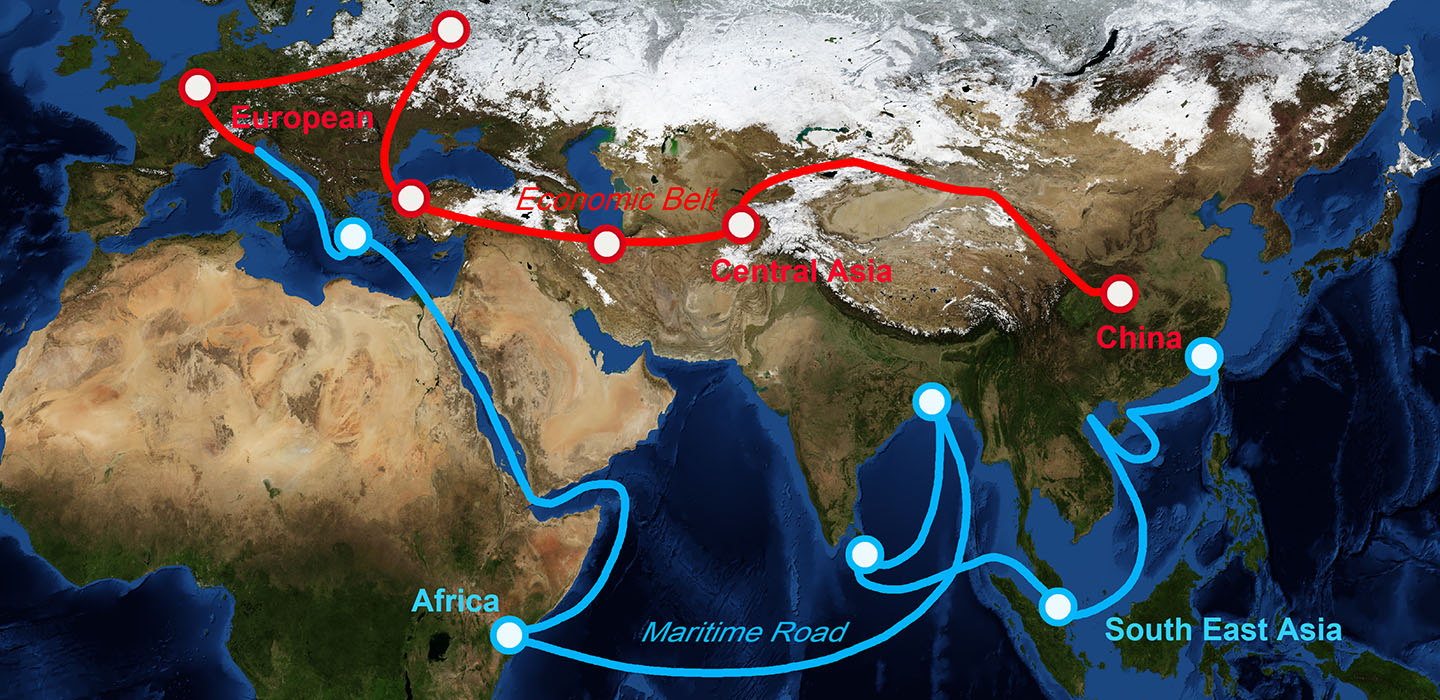
China’s meteoric rise as the second-largest economy in the world is one of the most significant developments of the last few decades. The country has consistently maintained high growth rates, driven by robust manufacturing, export-driven industries, and increasingly diverse sectors such as technology, finance, and consumer goods. As China’s domestic market expands, its economic footprint extends beyond its borders, influencing markets in Europe, Africa, Latin America, and even North America. This growth, supported by government policies like “Made in China 2025” and “Belt and Road Initiative,” aims to create a network of trade, infrastructure, and technological partnerships across the globe.
Technological Innovations: A New Frontier
China is making significant strides in emerging technologies. From artificial intelligence (AI) and quantum computing to 5G and renewable energy solutions, the nation is positioning itself as a global leader in technological innovation. Chinese companies like Huawei, Alibaba, and Tencent are at the forefront of these advancements, driving new business models and shaping global markets. Additionally, China’s commitment to investing in research and development (R&D) is fostering an environment that encourages innovation and the adoption of groundbreaking technologies, solidifying its place as a technological superpower.
Geopolitical and Diplomatic Expansion
China’s growing global influence is also evident in its increasingly assertive geopolitical and diplomatic strategies. Through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, China is creating new trade routes and fostering partnerships with countries across the globe. Furthermore, China’s involvement in global institutions, from the United Nations to the World Trade Organization, is further solidifying its role in shaping international policies and promoting its vision for a multipolar world order. Its growing influence is not only economic but also diplomatic, as China is becoming a key player in peace negotiations, global security matters, and international trade agreements.
Sustainability and Environmental Leadership
As China continues to grow, it also faces the challenge of balancing its industrial expansion with environmental sustainability. In recent years, the country has made significant progress in addressing climate change and investing in green technologies. China has become the world’s largest producer of solar panels and electric vehicles, and its commitment to carbon neutrality by 2060 demonstrates the country’s growing role in global environmental leadership. The integration of renewable energy sources, energy-efficient solutions, and the development of green technologies positions China as a leader in the global shift toward sustainability.
The Future of China’s Global Role
Looking ahead, China’s global influence is expected to continue expanding. Its growing investment in innovation, technological leadership, and strategic partnerships will further cement its position as a key player in the global economy. However, challenges remain, particularly in navigating its relationships with other global powers and managing its domestic issues. Nevertheless, China’s trajectory suggests that it will remain at the center of global affairs, driving future trends in technology, economics, and international relations.
In conclusion, understanding China’s global growing tendencies is essential for recognizing the direction in which the world is headed. As the country continues to evolve, its impact will be felt across every facet of society, from business and technology to politics and the environment. China’s future is poised to be one of unprecedented growth, and its role on the global stage will shape the world for generations to come.
Tendencies
China’s global economic and diplomatic reach has expanded significantly over the past few decades, establishing itself as a dominant force in nearly every continent. This influence is characterized by strategic investments, trade partnerships, and infrastructure development programs that have reshaped global economic patterns and political alliances. China’s approach is carefully tailored to the unique opportunities and challenges presented by each continent, resulting in diverse yet interconnected strategies that demonstrate Beijing’s far-reaching vision.
In Asia, China’s presence is most profound. Through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), Beijing has strengthened its ties with Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. Key projects such as the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) have provided critical infrastructure, connecting Chinese trade routes to strategic ports like Gwadar. In Southeast Asia, China has invested heavily in railways, bridges, and digital infrastructure, creating economic interdependence. Countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand have seen major inflows of Chinese capital in industries such as energy, technology, and logistics. Meanwhile, China’s influence in Central Asia has grown through strategic resource partnerships and development projects that link the region to Chinese markets.
In Europe, China has targeted key sectors through investment and technology cooperation. The “16+1 Initiative” was designed to foster economic ties with Central and Eastern European countries, focusing on infrastructure, transport, and trade expansion. Chinese companies have acquired stakes in critical ports such as Piraeus in Greece, providing a vital entry point for Chinese exports into Europe. Beijing has also cultivated strong trade relationships with major Western European economies like Germany and France, with particular emphasis on the automotive industry, renewable energy projects, and digital technology.
Africa has emerged as a focal point for Chinese investment, where Beijing has established itself as a major partner in infrastructure development, resource extraction, and telecommunications. Through projects such as railways in Kenya, ports in Djibouti, and energy initiatives in Nigeria, China’s presence has dramatically transformed the continent’s economic landscape. The Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) continues to play a key role in driving partnerships, emphasizing development financing, trade incentives, and educational exchange programs. By providing financial support with fewer political conditions than Western counterparts, China has gained substantial influence in African economic and political spheres.
In Latin America, China has emerged as a dominant trade partner, particularly in commodities such as soybeans, copper, and oil. Brazil, Argentina, and Chile have been primary beneficiaries of Chinese investments in agriculture, mining, and energy. China’s role in financing major infrastructure projects, including rail networks and renewable energy plants, has solidified its presence. The China-CELAC Forum has enhanced diplomatic ties and facilitated cooperation in areas such as technology, public health, and trade expansion.
In North America, while trade relations with the United States have faced political tensions, China maintains significant economic influence. Chinese investments in technology startups, real estate, and manufacturing remain substantial. Canada has become a strategic partner in resource trade, particularly in energy exports and agricultural goods. Despite geopolitical frictions, China’s economic ties with North America continue to expand through trade agreements and investment ventures.
In Oceania, China’s influence has grown rapidly, especially in the Pacific Islands, Australia, and New Zealand. Beijing has invested in infrastructure, energy, and telecommunications, strengthening economic ties in these regions. The Pacific Islands, in particular, have become a focal point for Chinese diplomacy, with Beijing providing development aid, trade incentives, and strategic partnerships in exchange for political alignment and support in international organizations.
Across continents, China’s diplomatic and economic strategies demonstrate common patterns: strategic investments in critical infrastructure, targeted partnerships in resource-rich regions, and the promotion of technology and digital connectivity. By fostering trade dependencies, China has extended its influence while avoiding direct confrontation. The Belt and Road Initiative has been the cornerstone of these efforts, promoting economic connectivity through a network of railways, highways, ports, and digital systems. Additionally, China has leveraged financial institutions such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) to support its strategic goals.
Through this comprehensive and adaptive approach, China has successfully established itself as a pivotal global player. By combining economic diplomacy with investment strategies that address both immediate development needs and long-term influence, Beijing has strengthened its presence across continents. As China’s economic reach continues to grow, its influence in shaping global trade patterns, political alliances, and technological advancements is set to remain a defining feature of international relations.
Nowadays
China’s global presence in 2025 is characterized by a complex web of economic, political, and infrastructural initiatives that span across all continents. With its growing influence, China has strategically positioned itself as a key partner in global development through a variety of projects and programs.
In Asia, China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) remains a cornerstone of its regional engagement. The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) continues to expand with new energy pipelines, railway lines, and industrial parks enhancing connectivity between Gwadar Port and China’s Xinjiang region. In Central Asia, Chinese investments in Kazakhstan’s Khorgos dry port have solidified it as a major logistics hub. Southeast Asia sees China’s influence through the high-speed railway connecting Kunming to Laos and Thailand, streamlining trade and tourism. In Indonesia, infrastructure projects like the Jakarta-Bandung high-speed rail project showcase Beijing’s commitment to regional connectivity. Additionally, China’s growing digital diplomacy has deepened ties with Singapore, Malaysia, and Vietnam through e-commerce collaborations and data infrastructure development.
In Europe, China’s economic footprint continues to expand via investments in major ports like Piraeus in Greece and Hamburg in Germany. The 17+1 Initiative, aimed at fostering cooperation with Central and Eastern European nations, has facilitated investments in railways, highways, and renewable energy projects. Italy’s participation in the BRI has enabled enhanced trade relations, particularly in luxury goods, agriculture, and energy. China’s partnerships with European financial hubs like London and Frankfurt have strengthened cross-border financial services, while Huawei’s expansion in 5G networks continues to shape Europe’s digital landscape.
In Africa, China has established itself as the continent’s largest trading partner. Through the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC), Beijing has funded major infrastructure projects such as railways in Kenya, highways in Ethiopia, and ports in Djibouti. Renewable energy initiatives have also expanded, with Chinese solar and wind power firms providing sustainable solutions across Africa. Additionally, Chinese-built industrial parks in countries like Nigeria, Angola, and Egypt are fostering local manufacturing growth.
In North America, despite geopolitical tensions, China maintains extensive economic ties, particularly in the technology and energy sectors. Chinese investments in electric vehicle battery supply chains, particularly in Canada’s lithium mining sector, have grown substantially. In the United States, Chinese firms continue to expand in e-commerce, digital payments, and AI research through strategic partnerships with Silicon Valley firms. Chinese tourism, education, and cultural exchange programs also remain key components of bilateral relations.
In Latin America, China’s influence is felt strongly in infrastructure development, mining, and agriculture. The China-Brazil Earth Resources Satellite program (CBERS) continues to provide critical data for environmental monitoring. In Argentina, China’s investment in lithium extraction has bolstered the country’s position as a key supplier for electric vehicle production. Infrastructure projects such as Panama’s port expansion and railway investments in Peru have enhanced China’s commercial presence in the region.
In Oceania, China’s partnerships with Australia and New Zealand remain economically significant. Despite diplomatic tensions, trade relations continue to thrive, particularly in the agricultural and mineral sectors. China’s strategic presence in Pacific Island nations has grown through funding for roads, ports, and renewable energy infrastructure, solidifying its influence in the region.
China’s role in the Arctic has also expanded, with Beijing declaring itself a “near-Arctic state” and investing in new shipping routes and research stations to enhance its presence in this strategically vital region. The Polar Silk Road initiative aligns with China’s broader BRI strategy, enabling smoother trade flows through the Arctic’s melting ice routes.
As 2025 unfolds, China’s global footprint reflects a carefully coordinated strategy of economic diplomacy, infrastructure development, and technological partnerships. With investments in renewable energy, digital infrastructure, and industrial growth, Beijing’s engagement with nations worldwide continues to evolve, positioning China as a pivotal force in shaping global economic dynamics.
Projects
The exposition of specific global projects of China is far not limitted by the following charts:
Asia
| Country | Project 1 | Project 2 | Project 3 | Commentary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Digital Silk Road Expansion | AI Innovation Centers | Renewable Energy Grid | Core hub driving global expansion strategies. |
| Pakistan | CPEC Road Networks | Gwadar Port Expansion | Karachi Circular Railway | Strategic trade routes enhancing regional connectivity. |
| India | Chennai Smart City Project | Gujarat Industrial Park | Digital Silk Road Collaboration | Despite tensions, strategic tech investments continue. |
| Indonesia | Jakarta-Bandung Railway | Morowali Industrial Park | Bali Data Center | Key Southeast Asian connectivity hub. |
| Thailand | China-Laos-Thailand Rail | E-commerce Logistics Hub | Bangkok Smart City Project | Digital and transport infrastructure development. |
| Vietnam | Hanoi Smart City | E-commerce Hub in Ho Chi Minh | Fiber Optic Network Expansion | Expanding tech partnerships and digital markets. |
| Philippines | Manila-Clark Railway | Davao Port Upgrade | AI Research Collaboration | Enhances transport and innovation hubs. |
| Malaysia | East Coast Rail Link | Kuantan Port Expansion | Digital Free Trade Zone | Strengthens regional logistics capabilities. |
| Singapore | Huawei AI Research Hub | Fintech Startup Investments | 5G Network Expansion | Asia’s digital innovation leader. |
| Saudi Arabia | NEOM Smart City | Red Sea Port Upgrade | Hydrogen Energy Plant | Aligns with Saudi Vision 2030 growth strategy. |
| Iran | Chabahar Port Development | Tehran Metro Expansion | Oil Refinery Upgrade | Focuses on trade expansion and energy security. |
| Turkey | Istanbul Finance Hub | Digital Silk Road Project | Middle Corridor Rail Expansion | Critical trade gateway connecting Asia and Europe. |
| Egypt | Suez Canal Zone Expansion | Cairo Metro Upgrade | Renewable Energy Farms | Boosts connectivity between Africa and the Mediterranean. |
| Bangladesh | Dhaka Metro Rail | Padma Bridge Expansion | Digital Connectivity Partnerships | Enhances urban infrastructure and digital trade. |
| Sri Lanka | Hambantota Port Development | Colombo Smart City Project | Renewable Energy Expansion | Critical link for maritime routes. |
| Myanmar | Kyaukpyu Port Expansion | Mandalay Industrial Zone | Oil & Gas Pipeline Projects | Strategic energy corridor. |
| Uzbekistan | Tashkent Metro Expansion | Silk Road Trade Hub | Digital Trade Corridor | Expands Central Asian connectivity. |
| Turkmenistan | Gas Pipeline Projects | Digital Infrastructure Investments | Renewable Energy Farms | Strengthens trade partnerships. |
| Mongolia | Mining Infrastructure | Renewable Energy Parks | Digital Connectivity Network | Expands resource trade. |
| Laos | China-Laos Railway | Mekong River Hydropower Project | Digital Silk Road Projects | Enhances trade through Southeast Asia. |
Europe
| Country | Project 1 | Project 2 | Project 3 | Commentary |
| Russia | Power of Siberia 2 Pipeline | Arctic Shipping Route | Joint Space Research Center | Expands strategic energy and Arctic trade links. |
| Germany | Duisburg Rail Freight Terminal | Renewable Energy Collaboration | AI Innovation Partnership | Strengthens EU-China trade corridors. |
| United Kingdom | London AI Research Hub | Digital Currency Partnerships | Renewable Energy Investments | Focuses on tech and clean energy partnerships. |
| France | Bordeaux Smart Port | Paris 5G Expansion | Hydrogen Energy Projects | Enhances digital and environmental innovation. |
| Italy | Trieste Port Expansion | Milan Digital Hub | High-Speed Rail Upgrade | Strengthens logistics and trade routes. |
| Greece | Piraeus Port Expansion | Athens Metro Upgrade | Energy Transition Investments | Key entry point for China’s European trade. |
| Spain | Valencia Port Expansion | Madrid Digital Innovation Hub | Renewable Energy Investments | Enhances trade and green energy. |
| Poland | Warsaw Logistics Hub | AI Innovation Park | Digital Trade Corridor | Strengthens Eastern European connectivity. |
| Netherlands | Rotterdam Port Expansion | Hydrogen Energy Network | Digital Infrastructure Partnerships | Secures China’s role in Western Europe. |
| Switzerland | Zurich AI Innovation Center | Digital Trade Partnerships | Renewable Energy Collaborations | Strengthens research and environmental ties. |
| Portugal | Lisbon Port Expansion | Renewable Energy Investments | Digital Infrastructure Development | Enhances Atlantic trade connectivity. |
| Sweden | Stockholm Smart Port | Digital Health Innovation Hub | Renewable Energy Grid | Focuses on sustainability and innovation. |
| Norway | Oslo Green Energy Hub | Arctic Trade Route Development | Digital Infrastructure Investments | Strengthens Arctic trade capabilities. |
| Denmark | Copenhagen AI Hub | Renewable Energy Projects | Data Infrastructure Networks | Expands digital innovation efforts. |
| Finland | Helsinki Smart Port | AI and Robotics Hub | Renewable Energy Grid | Enhances Finland’s role in digital innovation. |
| Austria | Vienna Smart City Project | Renewable Energy Partnerships | Data Infrastructure Expansion | Strengthens regional innovation. |
| Hungary | Budapest Smart City | Logistics Hub Development | Renewable Energy Farms | Focuses on trade and clean energy. |
| Czech Republic | Prague Digital Hub | AI Research Partnerships | Renewable Energy Networks | Advances environmental initiatives. |
| Romania | Bucharest Smart City | Digital Trade Corridor | Renewable Energy Investments | Expands Eastern European connectivity. |
| Bulgaria | Sofia Tech Park | Renewable Energy Investments | Digital Trade Partnerships | Strengthens tech and energy cooperation. |
Africa
| Country | Project 1 | Project 2 | Project 3 | Commentary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nigeria | Lagos-Calabar Coastal Railway | Abuja Smart City Project | Digital Infrastructure Network | Enhances regional transport and digital growth. |
| Kenya | Nairobi-Mombasa Railway | Lamu Port Expansion | Tech Innovation Park | Boosts East African connectivity. |
| South Africa | Huawei 5G Network Expansion | Johannesburg Industrial Park | Renewable Energy Projects | Focuses on digital and energy sectors. |
| Ethiopia | Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway | Industrial Parks | Wind Power Expansion | Expands China’s trade in the Horn of Africa. |
| Morocco | Tangier Port Expansion | Casablanca Smart City | Solar Energy Farms | Strengthens renewable energy efforts. |
| Algeria | Algiers Metro Upgrade | Oil Refinery Investments | Digital Education Program | Enhances resource and education sectors. |
| Angola | Luanda Port Expansion | Hydro Power Plant Projects | Industrial Park Investments | Focuses on energy and trade growth. |
| Ghana | Accra Digital Hub | Tema Port Expansion | Renewable Energy Grid | Strengthens digital and energy initiatives. |
| Egypt | Suez Canal Zone Expansion | Cairo Metro Upgrade | Renewable Energy Farms | Expands trade routes and clean energy. |
| Uganda | Kampala Industrial Park | Renewable Energy Development | Digital Trade Partnerships | Strengthens digital trade networks. |
| Tanzania | Dar es Salaam Port Expansion | Digital Infrastructure Projects | Renewable Energy Partnerships | Enhances trade and energy infrastructure. |
| Zambia | Copperbelt Mining Expansion | Renewable Energy Grid | Digital Innovation Park | Boosts mining and digital industries. |
| Congo (DRC) | Mining Infrastructure Development | Renewable Energy Partnerships | Digital Connectivity Network | Focuses on resource and tech growth. |
| Senegal | Dakar Smart City Project | Renewable Energy Investments | Digital Trade Partnerships | Enhances West African innovation. |
| Ivory Coast | Abidjan Port Expansion | Digital Innovation Park | Renewable Energy Farms | Strengthens tech and energy sectors. |
| Sudan | Khartoum Industrial Park | Digital Infrastructure Development | Renewable Energy Expansion | Expands trade and clean energy. |
| Cameroon | Douala Port Expansion | Renewable Energy Projects | Digital Innovation Hub | Enhances regional trade links. |
| Rwanda | Kigali Smart City | Renewable Energy Projects | Digital Trade Partnerships | Focuses on tech leadership in East Africa. |
| Mozambique | Maputo Port Expansion | Renewable Energy Farms | Digital Connectivity Partnerships | Expands trade and energy connectivity. |
| Namibia | Windhoek Digital Hub | Renewable Energy Investments | Industrial Park Development | Strengthens clean energy efforts. |
Latin America & Oceania
| Country | Project 1 | Project 2 | Project 3 | Commentary |
| Brazil | CBERS Satellite Program | São Paulo Metro Upgrade | Amazon Forest Monitoring Project | Enhances environmental and digital infrastructure. |
| Argentina | Lithium Mining Investments | Buenos Aires Port Expansion | Renewable Energy Grid | Strengthens EV supply chains. |
| Chile | Copper Mining Expansion | Santiago Smart Grid | Renewable Energy Partnerships | Focuses on mining and sustainable energy. |
| Mexico | Port of Manzanillo Upgrade | Industrial Park in Monterrey | Renewable Energy Plants | Expands North American trade. |
| Colombia | Bogota Metro Expansion | Renewable Energy Projects | Digital Connectivity Network | Focuses on tech and energy sectors. |
| Peru | Lima Smart City | Renewable Energy Grid | Mining Infrastructure Investments | Enhances environmental sustainability. |
| Venezuela | Oil Refinery Expansion | Renewable Energy Projects | Digital Infrastructure Partnerships | Balances energy and digital trade growth. |
| Ecuador | Quito Smart City Project | Renewable Energy Farms | Digital Trade Partnerships | Focuses on clean energy and tech expansion. |
| Cuba | Havana Digital Hub | Renewable Energy Networks | Industrial Park Development | Enhances energy and trade ties. |
| Bolivia | Mining Infrastructure | Renewable Energy Grid | Digital Connectivity Networks | Expands mineral resource trade. |
| Paraguay | Renewable Energy Investments | Digital Trade Corridor | Industrial Park Expansion | Focuses on clean energy growth. |
| Uruguay | Montevideo Digital Hub | Renewable Energy Projects | Industrial Park Investments | Strengthens digital and clean energy links. |
| Panama | Panama Canal Digital Upgrade | Renewable Energy Expansion | Digital Trade Partnerships | Enhances global trade links. |
| Costa Rica | Renewable Energy Grid | Digital Innovation Hub | Industrial Park Expansion | Focuses on environmental growth. |
| Australia | Rare Earth Mining | Renewable Energy Farms | Lithium Battery Supply Chains | Enhances mineral security for tech sectors. |
| New Zealand | Renewable Energy Investments | Digital Trade Corridor | Dairy Supply Chain Expansion | Strengthens agriculture and environmental ties. |
| Fiji | Suva Port Expansion | Road Networks Development | Renewable Energy Farms | Expands China’s presence in the Pacific. |
| Papua New Guinea | Mining Investments | Renewable Energy Projects | Digital Connectivity Networks | Strengthens trade and tech sectors. |
| Samoa | Renewable Energy Expansion | Digital Infrastructure Partnerships | Industrial Park Development | Expands clean energy and digital trade. |
| Tonga | Renewable Energy Investments | Digital Trade Networks | Industrial Hub Development | Focuses on environmental stability. |
Methods
China employs a multifaceted approach that combines economic leverage, strategic diplomacy, and technological integration to implement its global projects. Central to its strategy is the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aligns infrastructure investment with regional development needs while enhancing China’s trade networks. By offering concessional loans through state-owned banks, China ensures that partner countries gain access to large-scale funding, often bundled with favorable repayment terms to secure long-term influence. Chinese companies, frequently supported by state subsidies, dominate the engineering, procurement, and construction phases, ensuring cost efficiency and rapid project delivery.
China’s methods prioritize resource security and geopolitical advantage. Strategic investments in ports, railways, and energy pipelines create alternative trade routes that reduce reliance on traditional maritime chokepoints. Beijing actively negotiates bilateral agreements that embed technology transfer conditions, ensuring Chinese standards become integral to digital infrastructure development. This strategy amplifies China’s influence in sectors like 5G, AI, and smart cities, where technological dominance strengthens diplomatic ties.
China’s diplomatic strategy often blends economic incentives with cultural engagement. Training programs for local engineers and professionals facilitate knowledge transfer, while Confucius Institutes and educational exchanges reinforce China’s presence in host nations. This soft power element builds favorable public perception, ensuring smoother project execution and political support.
To mitigate risks, China employs risk-sharing mechanisms, joint venture models, and phased project rollouts. Pilot programs allow Beijing to assess a project’s viability before committing to full-scale investment. This incremental approach minimizes financial exposure and allows adjustments to local political or economic shifts. Additionally, China customizes project terms to align with each country’s development goals, fostering trust and reducing resistance.
In regions prone to instability, China frequently deploys security elements tied to critical infrastructure, ensuring project continuity. These measures range from Chinese-managed security firms protecting construction sites to diplomatic mediation for conflict resolution.
By combining financial power, technological dominance, and diplomatic engagement, China effectively integrates economic expansion with long-term geopolitical influence, ensuring its global projects align with broader strategic objectives.

